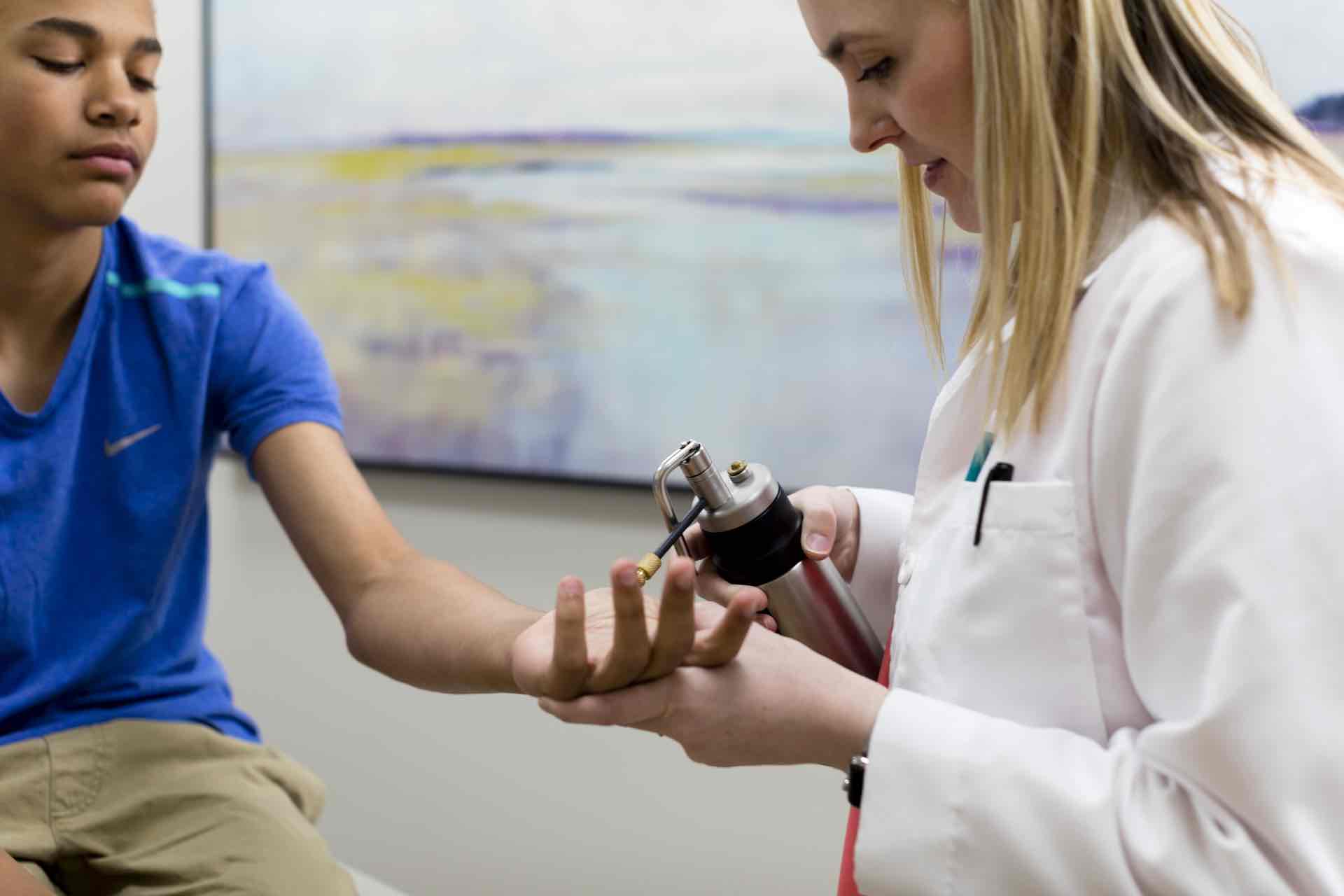Warts & Molluscum
What Are Warts?
There are many different types of viral infections of the skin that lead to different clinical presentations, but among the most common are warts and molluscum contagiosum.
Warts, or verruca, can present in a multitude of different ways, but all types of warts are caused by the various subtypes of the human papillomavirus. The most common types of warts include common warts, genital warts, plantar warts, and flat warts. Most people will experience some form of warts during their lifetime, and this pervasiveness is due to the virus’ ability to evade destruction by the host immune system. Warts can be transmitted via direct contact, indirect contact, or via autoinoculation. Once the virus is in place the virus promotes keratinocyte proliferation that leads to the ‘warty’ appearance clinically. Warts can be painful, interfere with activities, and cause social distress. Some types of warts, specifically genital warts and the strains of HPV that cause cervical cancer, can be prevented with the HPV vaccine. Treatment of warts depends on their location, appearance, and immune status of the patient. Typically the treatment is broken into two different categories: destructive and immunologic. Destructive methods can include cryotherapy, salicylic acid, cantharidin, 5-fluorouracil, and laser. Immunologic therapies can include imiquimod, candida antigen injection, or contact sensitization. Because some strains of the HPV virus can cause cancer, and because the clinical appearance of some warts can mimic squamous cell carcinoma, it is important to see a board-certified dermatologist if you have concerns about warts.
What Is Molluscum?
Molluscum contagiosum is a common skin condition most often seen in school-aged children, but which can also be found in sexually active adults, and in immunosuppressed individuals. It is caused by a type of poxvirus that infects the skin. As the name implies, the virus is very easily spread from person to person, usually by skin to skin contact but also by indirect contact with shared items such as towels. Autoinoculation is also common and scratching an affected area can lead to more of the lesions in other areas of the body. In adults, the virus is usually sexually transmitted. Clinically, the lesions of molluscum appear as small, smooth, dome-shaped pink bumps, typically with a dimple in the center. At times the lesions can get crusted, pustular, or have surrounding dermatitis, which can herald the resolution of that lesion. Children that have eczema, or people with altered immune systems, often have more extensive cases of molluscum. While they are often bothersome, the virus is otherwise relatively harmless. The natural course of molluscum is self-resolution over 1-2 years. Because they self-resolve, it is reasonable to leave them alone. However, for those wanting treatment, there are several modalities that can be tried including cryotherapy, canthardin, topical tretinoin, curettage, extraction and others.
Call 402-505-8777 to schedule an appointment!